Odoo内建服务器
包括HTTP、定时、live-chat服务器,使用多线程、多进程。
每一个HTTP请求都会创建一个线程,守护进程也会创建线程。存在GIL问题。
服务器
多线程服务器是默认服务器,不设置--worker或者设为0,使用多线程服务器。
【多进程服务器】
多进程服务器是用于生产的服务器。
设置了--worker且非0,使用多进程服务器。多进程是为Linux高度定制的,Windows中不可用。
1. 【进程池】
服务器启动时会创建一个进程池,HTTP请求由OS排队,等待worker处理。
2. 【事件驱动、定时任务、进程回收】
i. 【livechat】
1. 有一个专用的worker
2. 事件驱动的HTTP进程,运行在另一个端口(参数:--gevent-port)
3. 默认情况HTTP请求会使用默认的HTTP worker,必须部署代理,将/websocket/开头的请求转发到Livechat woker,odoo开启--proxy-mode,以便使用真实客户端的头而不是代理头。
ii. 定时任务也会启动一个进程
iii. 可配置的进程清理程序监视进程使用情况,并且可以杀死和重启失败的进程
【HTTPS】
Odoo以明文传输认证信息,因此必须使用HTTPS
【启用步骤】
1. 启动proxy mode,使用反向代理
2. 设置SSL终端代理
3. 设置代理自身
4. SSL终端代理应自动将非SSL重定向到SSL
【WSGI】
基础
Odoo可以部署为标准的WSGI应用程序
1. Wsgi运行脚本odoo-wsgi.example.py,需要定制修改脚本,以便直接在odoo.tools.config中配置
2. 需要同时运行内置服务器处理定时任务,但需要设置--no-http,或者设置http_enable=False,让它只处理定时任务
LiveChat
Livechat需要支持gevent的wsgi服务器,可以使用定时服务器来处理,将--no-http去掉,并确保/websocket/请求被重定向到该服务器
建议
在类Linux系统中,推荐使用多进程服务器以充分利用性能,即使用--workers=-1 和 --max-cron-threads=n参数
文件处理
静态文件
在开发环境中,Odoo直接将静态文件存储在了模块的static文件夹中,但对生产性能来说是不利的。应当由静态服务器处理。
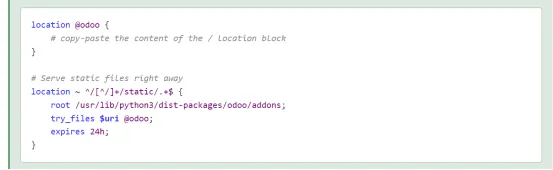
【配置Nginx处理静态文件】
1. 包安装的配置方式
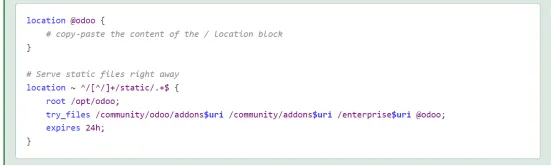
2. 源码安装的配置方式
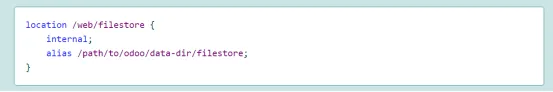
附件文件
不能直接通过web服务器访问,需要进行数据库查询,确定存储位置和权限。
尽管如此,一旦文件被定位且验证了权限,更好的办法是通过静态服务器代替Odoo提供文件。
需要启用X-Sendfile(apache)或X-Accel(nginx)扩展,同时使用odoo的--x-sendfile参数
Nginx配置
Web/database/manager只应用在开发环境中,生产环境应关闭,创建和维护数据库都应由管理员操作
one2many和many2many操作
(0, 0, { values })
创建新记录并关联(link to)到当前记录,使用给定的 values 字典创建新记录。
(1, ID, { values })
更新具有给定 ID 的已关联记录,使用 values 字典更新该记录。
(2, ID)
删除并删除具有给定 ID 的已关联记录,这会调用 unlink 方法来彻底删除目标对象以及与之相关联的链接。
(3, ID)
切断与具有给定 ID 的已关联记录之间的关系,不会删除目标对象本身,只删除它与当前记录之间的关联。
(4, ID)
关联到现有具有给定 ID 的记录,建立关系。
(5)
取消关联(unlink)所有关联的记录,类似于为每个已关联的记录使用 (3, ID)。
(6, 0, [IDs])
替换关联的记录列表,类似于首先使用 (5),然后为 IDs 列表中的每个 ID 使用 (4, ID)。
eg:
运行参数
--dev 开发模式
参数--dev xml
直接读取xml代码,而不用去数据库读取(不用更新模块)【注意:仅用于开发环境】

-i 安装模块
启动服务器前安装模块(逗号分隔的列表)
-u 更新模块
启动服务器前更新模块(逗号分隔的列表)
--without-demo 无需demo
不需要加载Demo数据
启动开发者模式
设置 → 启动开发者模式
开发者模式可以看到字段信息、记录元信息、操作安装模块等
调试工具Debug
"""Python Debugging
When facing a bug or trying to understand how the code works, simply printing things out can go a long way, but a proper debugger can save a lot of time.
You can use a classic Python library debugger (pdb, pudb or ipdb), or you can use your editor’s debugger.
In the following example we use ipdb, but the process is similar with other libraries.
Install the library:
pip install ipdb
Place a trigger (breakpoint):
"""
import ipdb; ipdb.set_trace()
Example
def copy(self, default=None):
import ipdb; ipdb.set_trace()
self.ensure_one()
chosen_name = default.get('name') if default else ''
new_name = chosen_name or _('%s (copy)') % self.name
default = dict(default or {}, name=new_name)
return super(Partner, self).copy(default)
"""
Here is a list of commands:
h(elp)[command]
Print the list of available commands if not argument is supplied. With a command as an argument, print the help about that command.
ppexpression
The value of the expression is pretty-printed using the pprint module.
w(here)
Print a stack trace with the most recent frame at the bottom.
d(own)
Move the current frame one level down in the stack trace (to a newer frame).
u(p)
Move the current frame one level up in the stack trace (to an older frame).
n(ext)
Continue the execution until the next line in the current function is reached or it returns.
c(ontinue)
Continue the execution and only stop when a breakpoint is encountered.
s(tep)
Execute the current line. Stop at the first possible occasion (either in a function that is called or on the next line in the current function).
q(uit)
Quit the debugger. The program being executed is aborted.
Now that your server is running, it’s time to start writing your own application
"""
架构
三层结构
ⅰ. 表现层
JS+HTML+CSS,OWL框架从Odoo15启用,后续可能会启用js
ⅱ. 逻辑层
方法和控制器,与另外两层交互
ⅲ. 数据层
ORM,映射模型到数据库并存储数据到磁盘
基本结构
module
├── models
│ ├── *.py
│ └── __init__.py
├── data
│ └── *.xml
├── __init__.py
└── __manifest__.py
a. 概念
- 由实现一个业务的一组对象、方法、数据、功能的集合
b. 文件结构
- Model(ORM)
- Data(View、Reporter)
- Controller
- Static
c. 注意
- manifest和init文件是必要的
- 模块至少依赖base
- 不能依赖全局变量;因为一个进程可能运行多个数据库
- Python文件改动需要重启服务器
数据
1. 模型
a. 定义(ORM)
from odoo import models
class TestModel(models.Model):
_name = "test_model" # 表名
_description = "table description" # 描述
_order = "create_date desc" # 排序
name = fields.Char(string="字段名", required=True, help="帮助信息", index=True,
copy=False, default="默认值")
"""
string (str, default: field’s name)
字段名
The label of the field in UI (visible by users).
required (bool, default: False)
必填
If True, the field can not be empty. It must either have a default value or always be given a value when creating a record.
help (str, default: '')
帮助/提示信息
Provides long-form help tooltip for users in the UI.
index (bool, default: False)
索引
Requests that Odoo create a database index on the column.
copy
复制时是否复制字段数据
default
默认值
"""
b. 环境变量
self.env.cr or self._cr is the database cursor object; it is used for querying the database self.env.uid or self._uid is the current user’s database id self.env.user is the current user’s record self.env.context or self._context is the context dictionary self.env.ref(xml_id) returns the record corresponding to an XML id self.env[model_name] returns an instance of the given model
c. 继承
ⅰ. inherit
- 继承父级,可以扩展、覆盖,重写方法
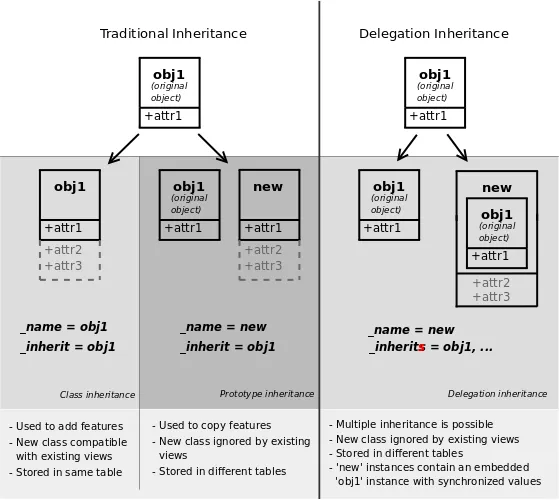
ⅱ. inherits
- 委派、代理(delegation)继承
- 允许记录链接到父级,提供透明地方式访问父级字段
ⅲ. 参考图片
d. 创建
api.model装饰器对于create方法是必须的,因为self的内容与创建上下文无关
@api.model
def create(self, vals):
# Do some business logic, modify vals...
...
# Then call super to execute the parent method
return super().create(vals)
ⅰ. 同时创建明细
from odoo import Command
def inherited_action(self):
self.env["test_model"].create(
{
"name": "Test",
"line_ids": [
Command.create({
"field_1": "value_1",
"field_2": "value_2",
})
],
}
)
return super().inherited_action()
e. 删除
ⅰ. 用ondelete好过直接覆盖unlink
ⅱ. 直接覆盖unlink可能导致卸载模块时的问题
@api.ondelete(at_uninstall=False)
def _unlink_if_user_inactive(self):
if any(user.active for user in self):
raise UserError("Can't delete an active user!")
f. 注意
- 重载父级方法时,保持返回值一致,以确保健壮性
2. 方法定义
需要注意,因为支持批量操作,所以self默认是multi的,也就是一个集合
因为系统的单个元素也支持迭代,所以我们不用考虑记录长度,直接用for迭代出来处理就可以
def action_do_something(self):
for r in self:
pass
3. 字段
a. many2one和x2many的建议
- many2one字段一般用_id后缀定义字段名称,比如partner_id
- x2many字段一般用_ids后缀定义字段名称, 比如order_line_ids,系统内也有用后缀的,比如move_lines
b. related和compute的关系
partner_id = fields.Many2one("res.partner", string="Partner")
description = fields.Char(related="partner_id.name")
# 上面的related等同于下面的compute:
partner_id = fields.Many2one("res.partner", string="Partner")
description = fields.Char(compute="_compute_description")
@api.depends("partner_id.name")
def _compute_description(self):
for record in self:
record.description = record.partner_id.name
c. 计算字段-compute
@api.depends('debit', 'credit') # 依赖字段
def _compute_balance(self):
# 计算逻辑
for line in self:
line.balance = line.debit - line.credit
###反向计算,添加后支持对计算字段设置值,设置值时会调用inverse####
from odoo import api, fields, models
class TestComputed(models.Model):
_name = "test.computed"
total = fields.Float(compute="_compute_total", inverse="_inverse_total")
amount = fields.Float()
@api.depends("amount")
def _compute_total(self):
for record in self:
record.total = 2.0 * record.amount
def _inverse_total(self):
for record in self:
record.amount = record.total / 2.0
【Tip】
- 请注意,反向方法在保存记录时被调用,而计算方法在其依赖项发生更改时被调用。
- 注意多层计算依赖【计算字段依赖其他计算字段】,会影响性能
d. 另一种计算-onchange
@api.onchange("partner_id")
def _onchange_partner_id(self):
self.name = "Document for %s" % (self.partner_id.name)
self.description = "Default description for %s" % (self.partner_id.name)
########可以弹出一个【非阻塞】提示###############
@api.onchange('provider', 'check_validity')
def onchange_check_validity(self):
if self.provider == 'authorize' and self.check_validity:
self.check_validity = False
return {
'warning': {
'title': _("Warning"),
'message': ('This option is not supported for Authorize.net')}
}
- onchange不影响数据库
- 只在form视图中触发
- 不要使用onchagne添加业务逻辑,因为它只在form view中触发,不会在记录创建时触发
e. Reference 字段
team_reference = fields.Reference(
selection=[('helpdesk.team', 'Helpdesk Team'),
('sales.team', 'Sales Team')],
string='Team Reference'
)
# 允许选择不同表的值,类似 m2o,但可以选择不同的表
f. 内置字段
id (Id)
The unique identifier for a record of the model.
create_date (Datetime)
创建时间
Creation date of the record.
create_uid (Many2one)
创建用户
User who created the record.
write_date (Datetime)
修改时间
Last modification date of the record.
write_uid (Many2one)
修改用户
User who last modified the record.
注意保留字段
如active
g. selection
ⅰ. 增加选项值
可以使用selection_add扩展selection字段
fields.Selection(selection_add=[
('dhl', "DHL")
]
ⅱ. 删除时的操作
selection的ondelete需要写成字典的形式,也支持lambda
delivery_type = fields.Selection(selection_add=[
('dhl', "DHL")
], ondelete={'dhl': lambda recs: recs.write({'delivery_type': 'fixed', 'fixed_price': 0})})
4. 排序
a. _order
直接在模型添加_order字段,指定要排序的字段的顺序
b. default_order
在tree加default_order,指定要排序的字段的顺序
c. 利用sequence
- 定义sequence字段
- 在_order中添加sequence排序
- 在tree view指定为handle widget
class Stage(models.Model):
_name = "crm.stage"
_order = "sequence, other_fields..." # 在_order中添加sequence排序
sequence = fields.Integer('Sequence', default=1, help="Used to order stages. Lower is better.")
<record id="crm_stage_tree" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">crm.stage.tree</field>
<field name="model">crm.stage</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<tree string="Stages" multi_edit="1">
<field name="sequence" widget="handle"/>
<field name="name" readonly="1"/>
<field name="is_won"/>
<field name="team_id"/>
</tree>
</field>
</record>
5. 数据文件
- csv、xml文件可以加载数据、定义界面视图
- 通过manifest文件定义引入
- 顺序是重要的,被依赖的模块需要定义在前面
- 在odoo中,csv的加载比xml更快
6. 权限
- 通过csv文件定义
id,name,model_id:id,group_id:id,perm_read,perm_write,perm_create,perm_unlink
access_test_model,access_test_model,model_test_model,base.group_user,1,0,0,0
- 未定义权限的模型无法被访问
7. domain
a. 定义
[('product_type', '=', 'service'), ('unit_price', '>', 1000)]
b. 用途
一般用来作为搜索条件
c. 与或非
- 与:默认是与,也可以用&
- 或: |
- 非: !
d. 使用建议
- 最好把与或非放前面,比如:
['|', ('product_type', '=', 'service'), ('unit_price', '>', 1000)]
- 系统会按顺序执行,与或非符号会对后面相邻的两个元素内的【表达式】进行计算
8. 约束
a. api.constrains约束
- 更新数据时会检查约束并提示
- 注意:会弹出提示,但不会阻塞数据更新
from odoo.exceptions import ValidationError
...
@api.constrains('date_end')
def _check_date_end(self):
for record in self:
if record.date_end < fields.Date.today():
raise ValidationError("The end date cannot be set in the past")
b. _sql_constraints
from odoo import models, api, exceptions
class MyModel(models.Model):
_name = 'my.model'
name = fields.Char(string='Name', required=True)
unique_field = fields.Char(string='Unique Field', required=True)
# SQL Constraint to ensure unique values in 'unique_field'
_sql_constraints = [
('unique_field_unique', 'UNIQUE(unique_field)', 'The value of unique_field must be unique.'),
]
- sql constraints效率比api.constrains更高
- sql constraints是直接在数据库级别设置的,所以会阻塞数据更新和创建
- 设置sql constraints时要确保数据库内没有违反约束的数据
9. float运算【比较和0判断】
使用odoo.tools.float_utils的 float_compare() 和 float_is_zero() 方法处理float运算!
10. |=运算符
【|=】
【odoo的这个运算符可以合并两个结果集】
previous_pickings = self.env['stock.picking']
previous_moves = self.move_lines.move_orig_ids
while previous_moves:
previous_pickings |= previous_moves.picking_id
界面
1. XML定义
a. action触发情况
- 通过点击菜单项(链接到具体操作)
- 通过点击视图中的按钮(如果它们与操作相关联)
- 作为对象的上下文操作
<record id="test_model_action" model="ir.actions.act_window">
<field name="name">Test action</field>
<field name="res_model">test_model</field>
<field name="view_mode">tree,form</field>
</record>
<menuitem id="test_model_menu_action" action="test_model_action"/>
2. 三级菜单
- 菜单一般由三级构成
<!-- 顶级菜单 APP界面(企业)/下拉界面(社区) -->
<menuitem id="test_menu_root" name="Test">
<!-- 二级菜单 -->
<menuitem id="test_first_level_menu" name="First Level">
<!-- 三级菜单 -->
<menuitem id="test_model_menu_action" action="test_model_action"/>
</menuitem>
</menuitem>
3. 视图
a. tree
<record id="crm_lost_reason_view_tree" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">crm.lost.reason.tree</field>
<field name="model">crm.lost.reason</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<tree string="Channel" editable="bottom">
<field name="name"/>
</tree>
</field>
</record>
b. form
<record id="crm_lost_reason_view_form" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">crm.lost.reason.form</field>
<field name="model">crm.lost.reason</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<form string="Lost Reason">
<sheet>
<div class="oe_button_box" name="button_box">
<button name="action_lost_leads" type="object"
class="oe_stat_button" icon="fa-star">
<div class="o_stat_info">
<field name="leads_count" class="o_stat_value"/>
<span class="o_stat_text"> Leads</span>
</div>
</button>
</div>
<widget name="web_ribbon" title="Archived" bg_color="bg-danger" attrs="{'invisible': [('active', '=', True)]}"/>
<div class="oe_title">
<div class="oe_edit_only">
<label for="name"/>
</div>
<h1 class="mb32">
<field name="name" class="mb16"/>
</h1>
<field name="active" invisible="1"/>
</div>
</sheet>
</form>
</field>
</record>
ⅰ. sublist - form的tree
<form>
<field name="description"/>
<field name="line_ids">
<tree>
<field name="field_1"/>
<field name="field_2"/>
</tree>
</field>
</form>
c. search
<search string="Tests">
<field name="name"/>
<field name="last_seen"/>
</search>
<search string="Test">
<field
name="description" string="Name and description"
filter_domain="['|', ('name', 'ilike', self), ('description', 'ilike', self)]"
/>
</search>
d. widget
<field name="many_line_ids" widget="many2many_tags" />
4. 按钮
<button type="action" name="%(test.test_model_action)d" string="My Action"/> <button type="object" name="action_do_somethign" string="My Action"/>
a. action按钮
触发一个action
b. object按钮
触发关联model对象中的方法
5. 设置动态的可见、只读、必填
- 可以设置字段依赖其他字段,动态的可见或者只读、必填 【invisible、readonly、required】
- 依赖的字段必须要在视图里出现
- 前端设置的只读readonly不会限制后端接口
<form>
<field name="description" attrs="{'invisible': [('is_partner', '=', False)]}"/>
<field name="is_partner" invisible="1"/>
</form>
6. 高亮
<tree decoration-success="is_partner==True"> <field name="name"> <field name="is_partner" invisible="1"> </tree>
7. stat button
8. 继承视图
<record id="inherited_model_view_form" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">inherited.model.form.inherit.test</field>
<field name="model">inherited.model</field>
<field name="inherit_id" ref="inherited.inherited_model_view_form"/>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<xpath expr="//field[@name='description']" position="after">
<field name="idea_ids" />
</xpath>
<field name="description" position="after">
<field name="idea_ids" />
</field>
</field>
</record>
expr
XPATH表达式
也可以用替代xpath标签来定位:
<field nane="field_name" />
position
插入的位置
可选:
1. inside
添加到定位的元素里
2. replace
替换定位的元素
3. before
插入到定位的元素前
4. after
插入到定位的元素后
5. attributes
为定位到的元素添加属性
内容为:
<attribute name="name">value</attribute>
9. kanban
<kanban>
<field name="state"/>
<templates>
<t t-name="kanban-box">
<div class="oe_kanban_global_click">
<field name="name"/>
</div>
<div t-if="record.state.raw_value == 'new'">
This is new!
</div>
</t>
</templates>
</kanban>
【如果不想让字段展示,可以定义到<templates>外面,如上面的state字段】
【每个字段有两个属性:value 和 raw_value】
1. value 是字段经过当前用户参数格式化后的值
2. raw_value 是直接从 read() 方法获取的未经处理的原始值
3. 这种设计提供了灵活性,用户可以选择使用格式化后的值或直接使用原始值
10. 密文
设置字段为密文
password="True"
模板
1. t-attf和t-att
- t-attf:
- t-attf是"t-attribute-format"的缩写,用于动态设置HTML元素的属性。
- 它允许你在属性值中使用动态的Odoo表达式。这意味着你可以在属性中使用像#{...}这样的表达式,这些表达式会在渲染时被实际的值替换。
- 例如,你可以使用t-attf来设置一个元素的class属性,类似于<div t-attf-class="#{condition ? 'class1' : 'class2'}">...</div>。
- t-att:
- t-att是"t-attribute"的缩写,用于设置静态的HTML元素属性。
- 它不支持在属性值中使用动态的Odoo表达式。你只能使用静态的字符串来设置属性。
- 例如,你可以使用t-att来设置一个元素的静态class属性,类似于<div t-att-class="'static-class'">...</div>。
总体而言,t-attf更加灵活,因为它允许在属性值中使用动态的表达式,而t-att用于静态的属性设置。选择使用哪个取决于你的需求,如果你需要动态地根据一些条件设置属性,那么使用t-attf可能更合适。
模块
结构
If your work tree looks like this:
estate
├── data
│ └── master_data.xml
├── demo
│ └── demo_data.xml
├── models
│ ├── *.py
│ └── __init__.py
├── security
│ └── ir.model.access.csv
├── views
│ └── estate_property_offer_views.xml
├── __init__.py
└── __manifest__.py
Your manifest should look like this:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
{
"name": "Real Estate",
"depends": [
...
],
"data": [
"security/ir.model.access.csv", # CSV and XML files are loaded at the same place
"views/estate_property_offer_views.xml", # Views are data too
"data/master_data.xml", # Split the data in multiple files depending on the model
],
"demo": [
"demo/demo_data.xml",
]
"application": True,
}
独立模块和链接模块
- 开发时要有模块化思维
- 如果功能属于不同模块,应当拆分出来
- 如果功能需要多个模块同时安装,可以用一个中间模块【依赖其他模块】来链接
- 这样可以保证模块可以独立安装
定义依赖
Python依赖
{
"name": "ISO 3166",
"version": "15.0.1.0.2",
"development_status": "Production/Stable",
"author": "Tecnativa, Creu Blanca, Odoo Community Association (OCA)",
"website": "https://github.com/OCA/community-data-files",
"license": "AGPL-3",
"depends": ["base"],
"external_dependencies": {"python": ["pycountry"]},
"data": [
'views/country_view.xml',
],
"installable": True,
}